India’s Connectivity Infrastructure: Tracking The Status Of Keystone Projects
We take a look at India’s connectivity infrastructure, including the status of proposed projects and how they link to an overall vision for the country’s logistics sector and economic development.
One of the crucial components that drive and sustain economic growth in a country is its infrastructure, which is critical for achieving manufacturing competitiveness.
Among key challenges obstructing progress in India’s infrastructure sector are its complicated land acquisition policies, implementation delays, and the risk of project overruns due to bureaucratic quagmire.
To address these, the current government has implemented policies to minimize such delays, simplify compliance procedures, and improve transparency to increase the pace of infrastructure projects.
Policies include simplification of land acquisitions, faster clearance/approvals from relevant authorities, using technologies, such as On-line Computerized Monitoring System and Pro Active Governance and Timely Implementation to improve project monitoring, and creating cost committees at the federal level to monitor cost overruns.
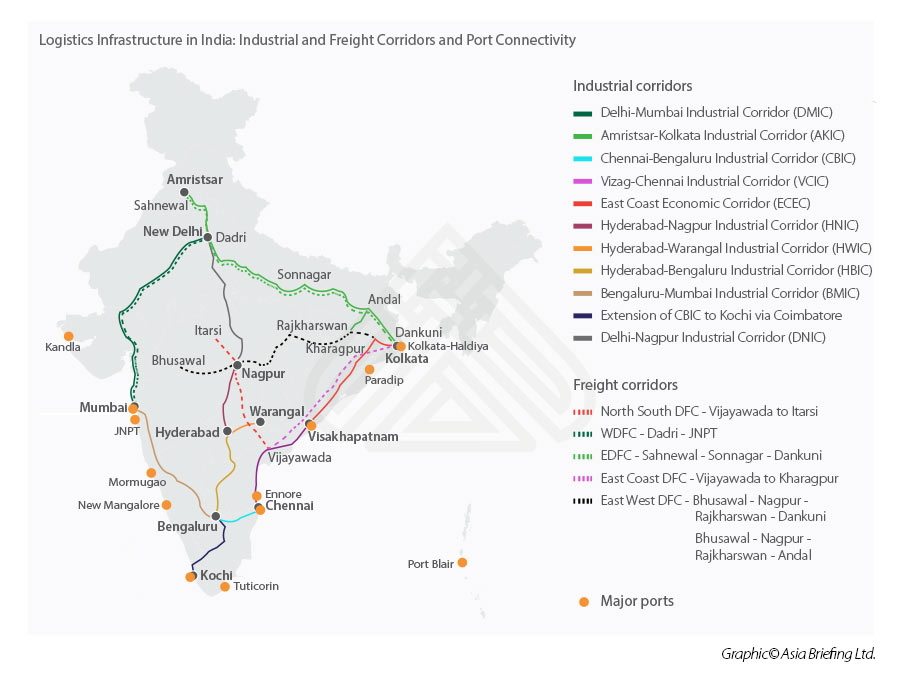
Industrial And Freight Corridor Projects
The government launched the National Infrastructure Pipeline for FY 2019-25, under which projects have been identified to construct, refurbish, strengthen, and expand roads networks, housing, urban development, railways, conventional power, renewable energy, and irrigation. Key programs will focus on highways and railways.
The Industrial Corridor Projects, part of the National Industrial Corridor program, is an example, and aligns with the development of industrial cities and improving inter-city connectivity so that they can compete with top global investment
destinations.
In addition, the government has also established a Special Purpose Vehicle for construction, operation, and maintenance of dedicated freight corridors under the Dedicated Freight Corridor program that aims to decongest the existing rail network by constructing dedicated tracks for goods trains. Currently, the construction work for both projects is in full swing.
Sagarmala Program For Port Development
For port infrastructure, since its launch, the Sagarmala Program (2015-2035) has identified more than 574 projects worth INR 6.01 trillion across areas of port modernization and new port development, port connectivity enhancement, port-linked industrialization, and coastal community development.
As of September 30, 2019, a total of 121 projects at a cost of INR 302.28 billion have been completed and 201 projects at a cost of INR 3.09 trillion are under implementation. The states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, among the top investment destinations in India, account for the country’s ports and sea routes.
Development Along Main Transportation Corridors
India’s federal government has approved infrastructure proposals worth INR 77.25 billion (approx. US $1.06 billion) to set up greenfield industrial cities with connectivity to major transportation corridors, such as the eastern and western dedicated freight corridors, expressways, national highways, ports, and airports.
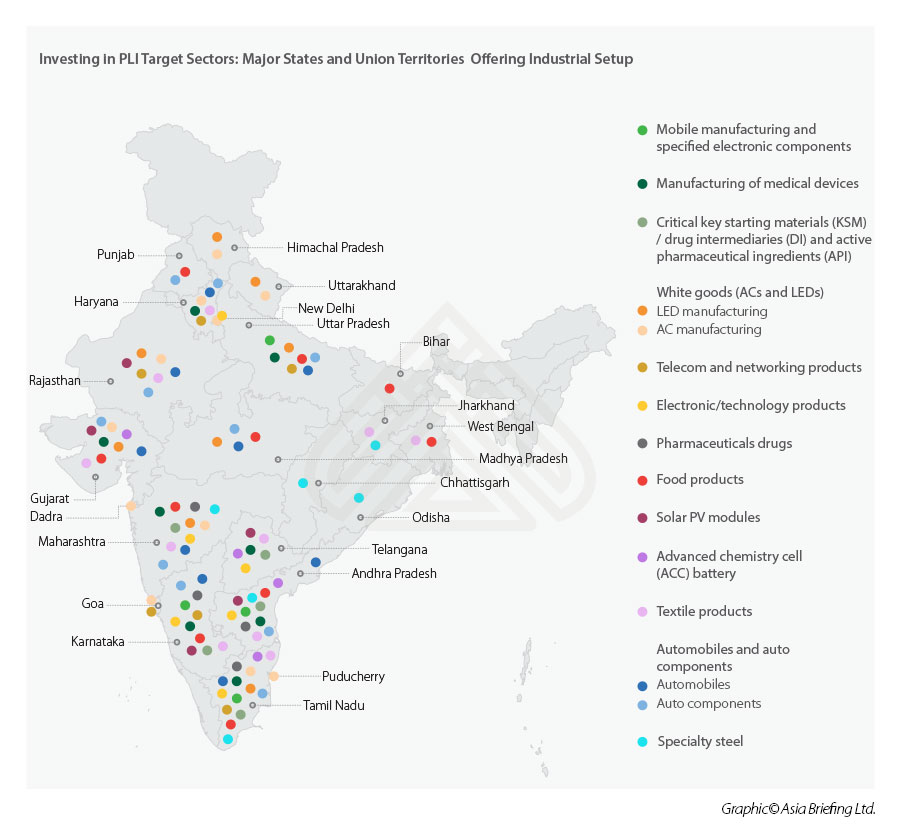
This aligns with India’s focus on developing industrial hubs across the country to effectively participate in the global supply chains (see map below for industrial hubs expected to benefit from the Production-Linked Incentive schemes).
The industrial corridors will integrate industries with necessary infrastructure, create employment opportunities, as well as boost export avenues by ensuring smooth access to production units, decreased transportation and communications costs, improved delivery times, and reduction in inventory costs.
In terms of their cascading effect – these corridors will facilitate setting up industrial townships, educational institutions, and hospitals, and in the process raise the standards of human development. In many regions, this would check the pace of outmigration and promote talent retention in lower tier cities.
Mapping India’s Infrastructure Connectivity
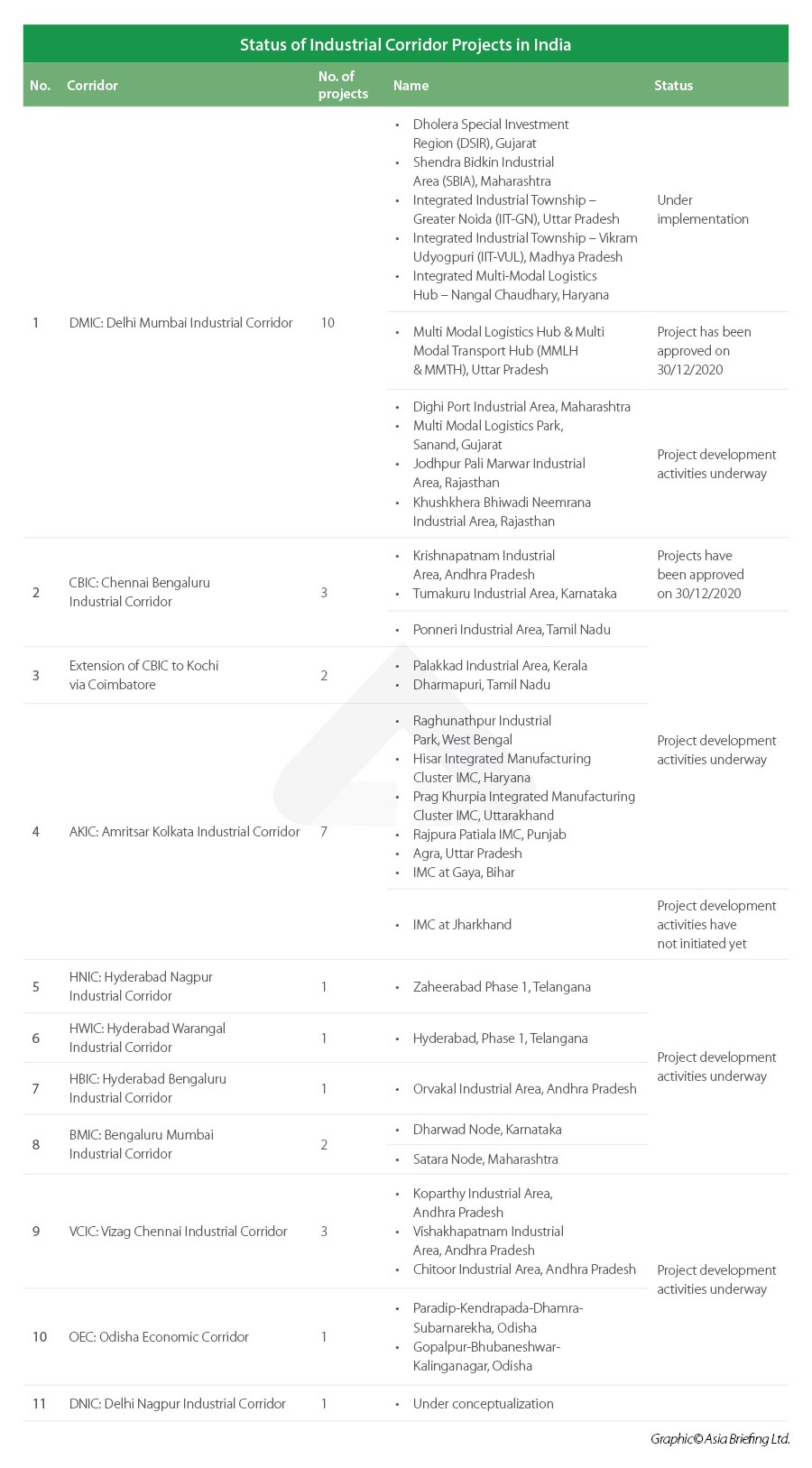
Status Of India’s Industrial Corridor Projects
National Infrastructure Pipeline
The National Infrastructure Pipeline or NIP is a group of infrastructure projects worth approximately US $1.9 trillion and aimed at improving the ease of living and business environment in India.
Initially, the NIP was earmarked for 6,835 projects, but has expanded to include 7,722 projects as of writing this publication. There are 1,699 projects under development across 34 sub-sectors, according to the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance. NIP investment opportunities are available in transport, logistics, energy, water and sanitation, communication, social infrastructure, and commercial infrastructure.
The NIP vision seeks to make India a US$5 trillion economy by 2024-25. Regardless of the sustainability of this estimated timeline, in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the pipeline includes economic and social infrastructure projects across vital sectors like energy, roads, urban development, and railways.
Cumulatively, these projects will ensure broad-based and inclusive growth across the country, strengthen agricultural and rural infrastructure, and increase sources of financing for infrastructure to promote investor confidence.
The big picture here is to project India’s infrastructure growth and development as an attractive proposition for foreign investors as this needs huge amounts of capital investment.
So far, the government is marketing opportunities in this area through the India Investment Grid (IIG) and National Investment & Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) by providing transparent data sets and facility for monitoring investment opportunities.
The Indian government has also enacted development schemes to provide momentum to arterial projects and make them viable options for national and international investors. These schemes like AMRUT, BHARATMALA, National Solar Mission, Railways Station Development Program, Smart City Mission, SAGARMALA, etc. are sponsored through federal, state-specific, or joint mechanisms and offer investment opportunities through public-private partnerships, procurement contracts, and various other modes of development.
Policy reforms through investment schemes, such as permission of 100 percent FDI under the automatic route in a wide variety of sectors, also serve to ease access to the India opportunity.




Comments